Green Computing: How Tech Is Fighting Climate Change in 2030
1. Why Technology Must Go Green Now
Technology accounts for approximately 4% of global CO₂ emissions, and the number is rising. Data centers, AI training, cloud infrastructure, and electronics manufacturing have created a massive digital carbon footprint. The energy crisis paired with climate change forces technology to evolve into a greener, cleaner ecosystem.
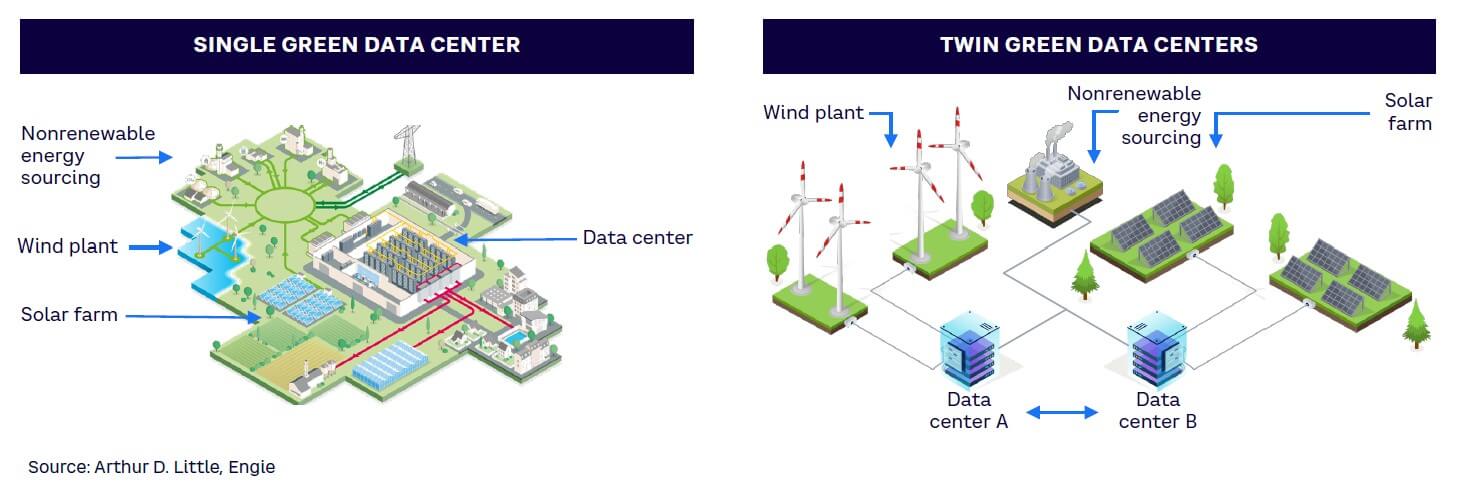
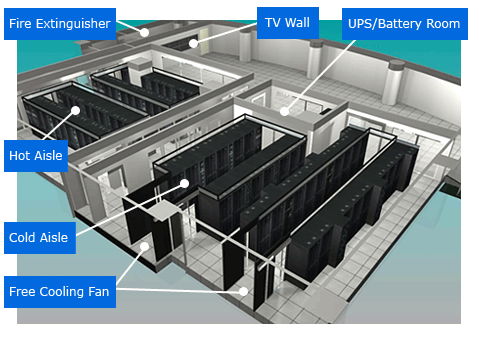
2. Green Data Centers: The Heart of Sustainable Computing
Data centers run the digital world — but they also consume power equal to small cities. By 2030, companies are building renewable-powered data centers, using:
-
Solar
-
Wind
-
Geothermal
-
Hydropower
And adopting innovations like:
-
Liquid cooling
-
Immersive cooling
-
Waste heat recycling
-
AI-based energy optimization
3. Renewable Energy-Powered Computing
Cloud providers, AI developers, and major tech corporations now operate using 100% renewable electricity. Solar panels, large wind farms, and hydro-powered facilities drastically reduce computing’s carbon footprint.
4. The Rise of Low-Power Chips & Eco-Friendly Hardware
Hardware is becoming up to 70% more energy-efficient thanks to:
-
Low-power ARM & RISC-V processors
-
3D chip stacking
-
AI-based power management
-
Biodegradable and recyclable components
-
Modular, easy-to-repair designs
5. Green Artificial Intelligence
AI is both a heavy energy consumer and a powerful sustainability tool. By 2030, AI helps:
-
Optimize energy grids
-
Predict climate disasters
-
Reduce food waste
-
Manage air pollution
-
Improve agriculture efficiency
-
Lower its own computing load
6. The Circular Economy: Reducing E-Waste
With 57 million tons of e-waste generated every year, companies are now enforcing:
-
Right-to-repair
-
Recycling programs
-
Refurbished electronics
-
Reusable, modular components
The circular economy keeps devices in use and out of landfills.
16. The Hidden Environmental Cost of the Digital World
Most people think of pollution as factories, vehicles, or power plants — but the digital world is becoming one of the biggest invisible contributors to climate change.
The Hidden Emissions Include:
✔ Energy used in AI training
Training a single large AI model can emit as much carbon as five cars over their entire lifetime.
✔ Cloud infrastructure
Millions of servers run 24/7 — even when demand is low.
✔ Consumer electronics manufacturing
Mining rare-earth materials is extremely polluting.
✔ Wireless networks
5G infrastructure adds huge energy demands.
✔ Streaming platforms
Streaming a 4K movie for 2 hours uses as much energy as running a refrigerator for a day.
As we move toward a fully digital society, the carbon footprint grows unless we redesign everything around sustainability.
17. The Future of Sustainable Software: Algorithms That Save the Planet
While hardware is becoming more efficient, software is undergoing a quiet sustainability revolution too.
🧩 What Makes Software “Green”?
Green software aims to:
-
Use fewer computational cycles
-
Reduce server load
-
Optimize memory consumption
-
Minimize GPU usage
-
Use energy-efficient data structures
-
Avoid unnecessary network calls
🌱 Examples of Green Software in 2030
-
Smart energy mode for apps
-
AI-optimized rendering in mobile games
-
Eco-friendly streaming codecs reducing bandwidth
-
Web apps that auto-minimize power usage
Green software engineering is now a required skill in top companies.
18. Water Usage: The Hidden Crisis of Data Centers
Most people don’t know this, but data centers consume massive amounts of fresh water for cooling.
🌊 Water Usage Statistics
-
A single mid-size data center can use 3–5 million gallons per day — equivalent to a small city.
-
AI training significantly increases cooling requirements.
-
As temperatures rise globally, cooling demands rise too.
💧 Green Solutions in 2030
-
Closed-loop water systems
-
Non-potable water recycling
-
Atmospheric water harvesting
-
Underwater data centers
-
Liquid and immersion cooling (no water needed)
Reducing water usage is now becoming just as important as reducing electricity.
19. Green Quantum Computing: The Next Sustainable Breakthrough
Quantum computers promise to solve complex climate problems with a tiny fraction of the energy that classical supercomputers require.
⚛️ Quantum Computing Helps Fight Climate Change By:
-
Modeling CO₂ absorption
-
Designing new eco-friendly materials
-
Predicting climate disasters
-
Accelerating battery discovery
-
Optimizing supply chains
By 2030, quantum computing will be a pillar of environmental research.
20. Smart Buildings Powered by Green Computing
Buildings are becoming living ecosystems powered by green technology.
🏢 Key Features:
-
AI-controlled lighting
-
Automated temperature control
-
Renewable-powered HVAC
-
Autonomous window shading
-
Predictive energy use
-
Grid interaction through smart meters
Smart buildings cut energy waste by 30–60% while improving comfort.
21. Carbon-Negative Technology Companies
Some companies are going beyond “carbon-neutral” by becoming carbon-negative — removing more CO₂ from the atmosphere than they produce.
🌍 How They Achieve This:
-
Renewable-powered data centers
-
Tree planting at scale
-
Carbon capture and storage
-
Recycled and modular devices
-
AI-optimized global logistics
-
Electrified transportation fleets
These companies lead the transformation toward a net-zero future.
22. Digital Twins for Climate Simulation
Digital twin technology allows real-time modeling of:
-
Oceans
-
Forests
-
Farmland
-
Entire cities
-
Wildlife migration
-
CO₂ emissions
-
Energy consumption
Scientists can simulate:
-
Storm paths
-
Flood risks
-
Infrastructure load
-
Renewable energy distribution
In 2030, digital twins are helping governments predict and prevent environmental damage.
23. Blockchain for Sustainability Tracking
Blockchain is often criticized for pollution, but in 2030, the technology is becoming a green infrastructure tool.
🌿 Environmental Uses
-
Tracking carbon credits
-
Verifying supply chain sustainability
-
Eliminating counterfeit eco-products
-
Transparent ESG reporting
-
Monitoring wildlife conservation
Green blockchains use:
-
Proof-of-stake
-
Renewable-powered nodes
-
Carbon-offset validators
Blockchain has moved from polluter → protector.
24. The Eco-Impact of Remote Work in 2030
Remote work reduces:
-
Office energy usage
-
Traffic emissions
-
Construction footprint
-
Commute pollution
But increases:
-
Home energy usage
-
Device manufacturing demand
-
Network load
Green computing solutions balance both using:
-
Low-power laptops
-
Renewable home energy
-
Cloud-based collaboration
-
Efficient video streaming
Remote work helps the planet when done sustainably.
25. Biodegradable & Plant-Based Electronics
This is one of the most exciting innovations of the decade.
By 2030, researchers have developed:
-
Plant-based circuit boards
-
Mushroom-root packaging
-
Paper-based processors
-
Organic memory cells
-
Biodegradable batteries
These devices decompose naturally after disposal — eliminating e-waste.
26. Green Edge Computing: Processing Data Locally
Instead of sending all data to the cloud, edge computing processes information locally.
🌎 Why This Helps the Environment:
-
Fewer long-distance data transfers
-
Lower cloud server usage
-
Faster reaction times
-
Reduced energy for cooling
-
Smaller carbon footprint
Smart cars, smart cities, and IoT devices use edge processing heavily in 2030.
27. Eco-Friendly AI Training: The New Standard
Companies now use:
-
Renewable-powered AI clusters
-
Efficient model architectures
-
Distillation to shrink models
-
Reusable training datasets
-
GPU recycling programs
-
Low-precision computing (FP8, INT4)
This reduces energy use by up to 80%.
28. Carbon Footprint Dashboards for End Users
Tech companies are now transparent.
Your phone, laptop, apps, and cloud dashboard show:
-
Your CO₂ usage
-
Energy consumed
-
Pollution saved using eco modes
Consumers are empowered to make greener choices.
29. Countries Leading the Green Computing Revolution
🇫🇮 Finland
Powered by hydro + geothermal, hosting the world’s greenest data centers.
🇮🇸 Iceland
Runs nearly 100% renewable-powered AI clusters.
🇯🇵 Japan
Leads energy-efficient chip technology.
🇩🇰 Denmark
Top in wind-powered computing infrastructure.
🇺🇸 USA
Major investments in solar farms and high-efficiency data centers.
🇮🇳 India
Solar-powered rural data networks and green mobile towers.
30. Green Computing Jobs — The Careers of the Future
By 2030, sustainability is a core skill in tech.
Top Green Tech Careers:
-
Environmental data engineers
-
Green cloud architects
-
Sustainable software developers
-
Climate-focused AI scientists
-
Renewable energy IoT technicians
-
Green cybersecurity analysts
-
Circular economy product designers
These careers are in massive demand globally.