How Bluetooth Works: A Simple, Complete Guide
Bluetooth is one of the most common technologies in the world today. You use it when you connect your headphones, pair your smartwatch, play music in your car, or even track your lost device. Yet, most people still don’t understand what Bluetooth actually is or how it really works.
In this in-depth guide, we break down Bluetooth in the simplest way possible — from its history to how it sends data, how devices pair, how secure it is, and how it is evolving into the future.
Let’s dive in.
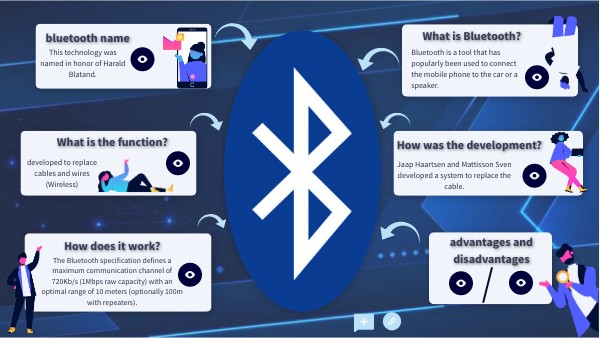
1. What Is Bluetooth? (In Simple Words)
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless communication technology that allows two or more devices to connect and exchange data without cables. It uses radio waves, but they operate at a very low power and cannot travel long distances.
Bluetooth is perfect for things like:
-
Headphones
-
Speakers
-
Smartwatches
-
Fitness trackers
-
Keyboards & mice
-
Cars & infotainment systems
-
TVs
-
Game controllers
Its biggest strengths are simplicity, low energy use, and quick pairing.
2. A Quick History of Bluetooth
The idea of Bluetooth began in the 1990s when engineers needed a way to connect devices without cables.
It was named after Harald “Bluetooth” Gormsson, a Viking king who united Denmark — just like Bluetooth unites devices.
Since then, Bluetooth has improved through different versions:
-
Bluetooth 1.0 – basic communication
-
Bluetooth 2.0 – faster speeds
-
Bluetooth 4.0 – Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
-
Bluetooth 5.0 – longer range & better audio
-
Bluetooth 5.3 – efficient, stable, IoT-friendly
Today, Bluetooth is used in over 5 billion devices every year.
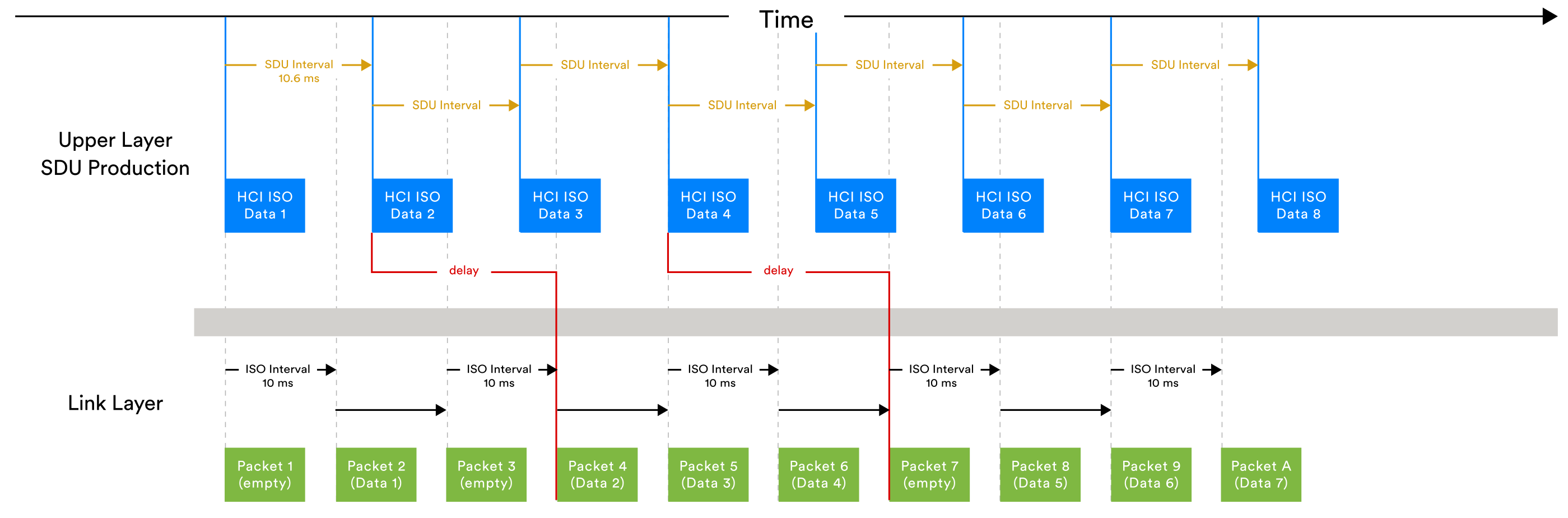
3. How Bluetooth Actually Works (Simple Explanation)
Like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth uses radio waves — but it works differently.
✔ Frequency
Bluetooth uses the 2.4 GHz ISM band, the same band as Wi-Fi and microwaves.
✔ Short Range
Most Bluetooth devices work within 10 meters (33 feet), though advanced devices can reach 50–100 meters.
✔ Low Power
Bluetooth uses minimal energy, which makes it perfect for battery-powered gadgets.
✔ Small Data Packets
Bluetooth sends tiny packets of information extremely quickly.
This makes it ideal for:
-
Audio
-
Notifications
-
Sensor data
-
Input devices
But not good for:
-
Large downloads
-
High-bandwidth tasks like streaming video
4. Bluetooth Pairing: How Devices Connect to Each Other
Pairing is the process of creating a secure connection between two Bluetooth devices.
Here’s how it works:
Step 1: Discovery (Finding Devices)
Your device scans the area for Bluetooth signals.
Step 2: Authentication (Approving the Connection)
You select the device you want to pair with.
Sometimes you enter a PIN or confirm a code.
Step 3: Bonding (Saving the Connection)
Devices exchange cryptographic keys to securely communicate.
Step 4: Connection
Once bonded, the link stays active until you disconnect or move out of range.
This entire process takes less than 5 seconds for most modern Bluetooth devices.
5. Bluetooth Profiles: How Devices Know What To Do
Bluetooth doesn’t do the same thing for all devices.
It uses profiles, which are like special skill sets.
Some common Bluetooth profiles include:
🎧 A2DP — For stereo audio
Used by headphones, speakers, and cars.
🎤 HFP / HSP — For calls
Used in car systems, earbuds, and headsets.
⌨️ HID — For keyboards and mice
Used in wireless computer accessories.
🖼 OBEX — For file transfers
Used in older phones (before Wi-Fi became dominant).
⚕️ BLE GATT — For sensors
Used by smartwatches, fitness bands, and medical devices.
Bluetooth automatically chooses the correct profile depending on the device.
6. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): The Game-Changer
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) is one of the biggest improvements in Bluetooth history.
Why BLE is important:
-
Uses much less power
-
Extends battery life
-
Perfect for IoT devices
-
Great for health sensors
-
Enables real-time tracking
BLE powers:
-
AirTags & smart trackers
-
Smart home devices
-
Fitness trackers
-
Temperature sensors
-
Security systems
This is why your smartwatch can last days, even though it’s always connected.
7. How Bluetooth Sends Data
Bluetooth uses several technical methods (simplified explanation):
✔ Frequency Hopping
Bluetooth switches frequencies 1,600 times per second to avoid interference.
✔ Small Packets
Short, quick bursts of data reduce lag.
✔ Master–Slave System** (now called Central–Peripheral)
One device is the controller (phone), and the other follows (headphones).
✔ Secure Encryption
Data is encrypted to prevent unauthorized access.
This setup ensures:
-
Stable connection
-
Low power use
-
Good audio quality
-
Reliable sensor data
8. How Bluetooth Audio Actually Works
Bluetooth converts music or voice into digital packets, sends them through radio waves, and reconstructs them on your headphones.
This process uses audio codecs, such as:
-
SBC (default codec)
-
AAC (common in iPhones)
-
aptX (high-quality audio)
-
LDAC (hi-res audio)
-
LC3 (new standard for Bluetooth 5+)
The LC3 codec offers:
-
Better quality
-
Lower power use
-
Fewer audio dropouts
It’s becoming the new standard for 2030s Bluetooth audio.
9. Bluetooth Range Explained
Range depends on:
-
Bluetooth version
-
Obstructions
-
Device class
-
Antenna size
👉 Typical ranges:
-
Class 3: 1 meter
-
Class 2: 10 meters (most phones and earbuds)
-
Class 1: 100 meters (commercial equipment)
Bluetooth 5 improved range and stability significantly.
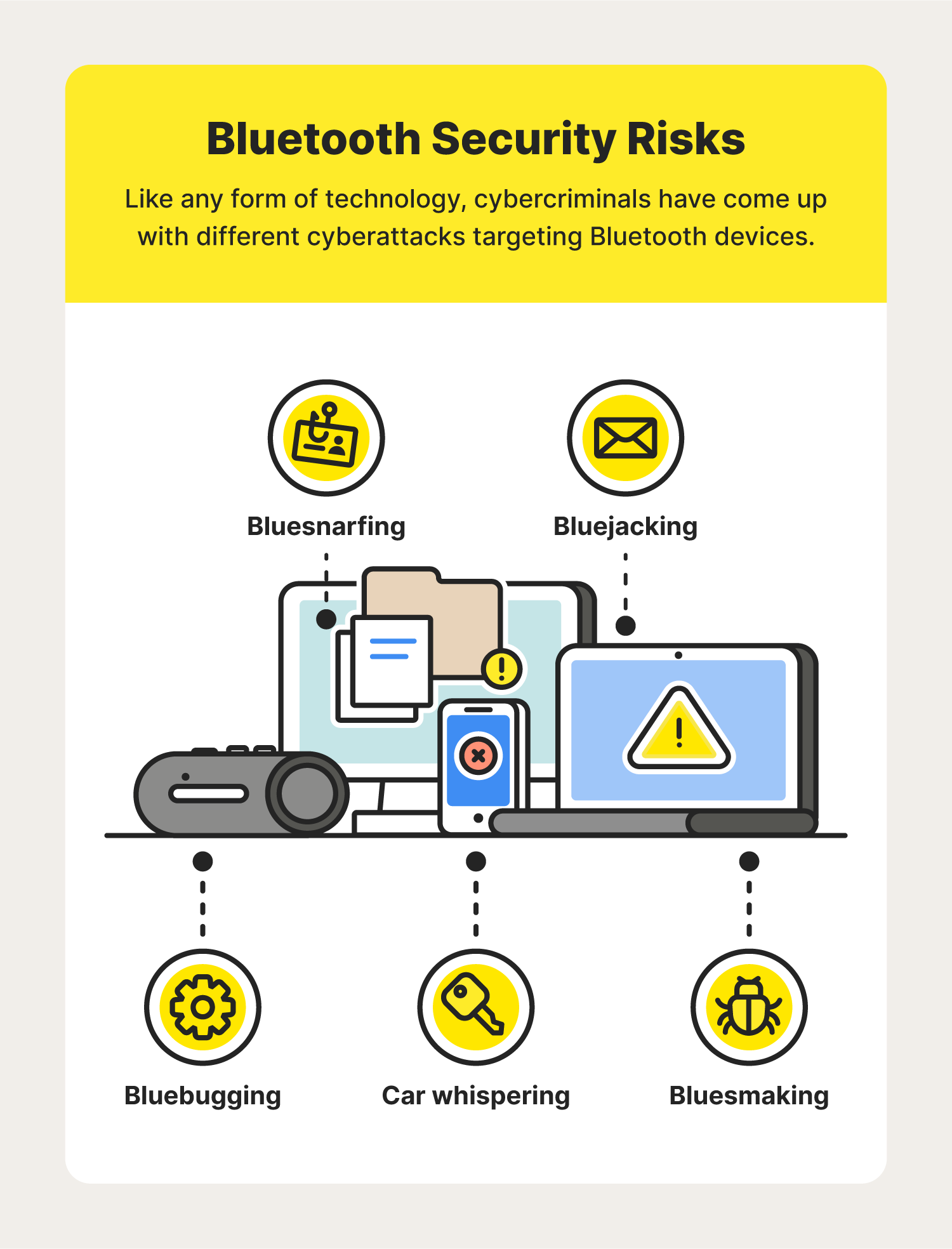
10. Bluetooth Security: Is It Safe?
Bluetooth uses strong encryption, but it’s not perfect.
Common Threats
• Bluejacking
Sending unwanted messages.
• Bluesnarfing
Stealing data from unprotected devices.
• Bluebugging
Taking control of a device.
How Bluetooth Protects You
-
Device authentication
-
Encryption keys
-
Frequency hopping
-
Limited range
-
Permission-based connections
-
Blocking unknown devices
Modern phones are very secure, but public areas can still pose risks.
11. Real-Life Uses of Bluetooth in 2025
Bluetooth is everywhere.
🎧 Audio and Music
Headphones, speakers, earbuds.
🚗 Cars
Hands-free calling, audio streaming, wireless Apple CarPlay & Android Auto.
⌚ Wearables
Smartwatches, glucose monitors, fitness trackers.
🏠 Smart Homes
Door locks, lights, motion sensors.
🖥 Computers
Mice, keyboards, printers.
🛒 Retail & Tracking
Bluetooth beacons showing location & promotions.
The Bluetooth world is growing every year.
12. The Future of Bluetooth
Bluetooth will continue improving, and the next versions will include:
✔ Longer range
✔ More stable connections
✔ Ultra-low energy usage
✔ Better audio quality
✔ Faster pairing
✔ Higher security
✔ Advanced IoT support
Bluetooth 6.0 is expected to focus on:
-
Smart cities
-
Healthcare devices
-
Industrial automation
-
Real-time sensors
Bluetooth will remain a core wireless technology for decades.
⭐ Conclusion
Bluetooth may seem simple, but it is one of the most powerful and widely-used technologies in modern life. It works by using low-power radio waves to connect devices quickly and securely, making everything from headphones to smartwatches function seamlessly.
Its low energy usage, improved range, solid security, and constant innovation ensure Bluetooth remains essential in the future of wireless communication.