Introduction: Why Kubernetes Security Matters More Than Ever in 2026
Kubernetes has become the backbone of modern cloud-native applications. As organizations scale clusters across multi-cloud and hybrid environments, Kubernetes security practices. Misconfigurations, supply-chain attacks, exposed APIs, and weak access controls remain the top causes of breaches.
In 2026, Kubernetes security practices—it is a core operational requirement. This guide covers the best Kubernetes security practices and tooling to protect workloads, data, and infrastructure in production environments.
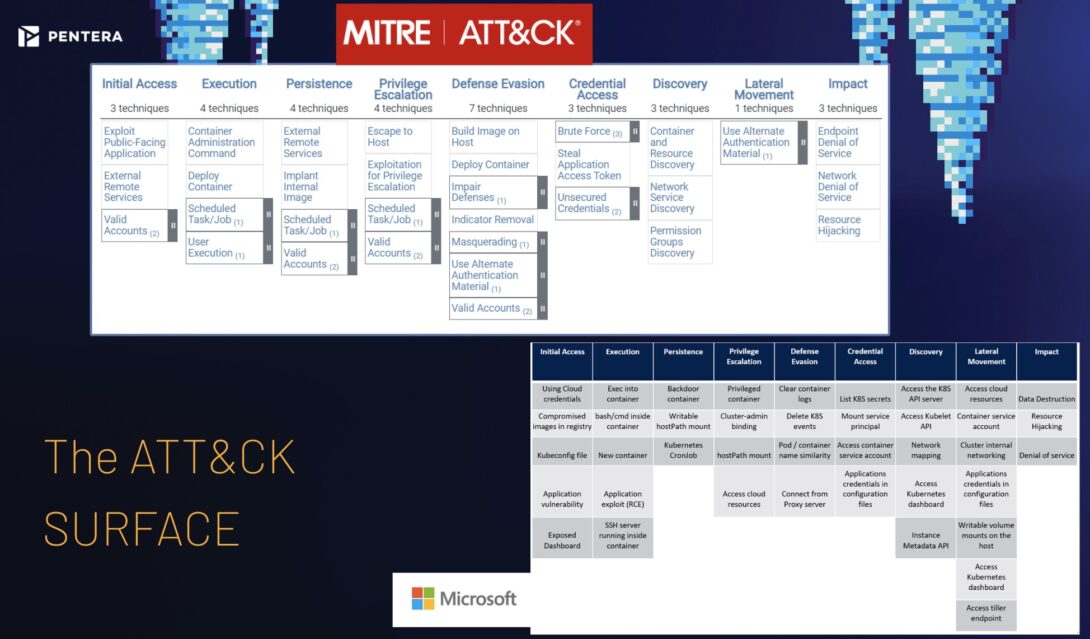
Key Kubernetes Security Threats in 2026
Common threats include:
-
Misconfigured RBAC permissions
-
Exposed Kubernetes APIs
-
Vulnerable container images
-
Supply-chain attacks
-
Runtime container exploits
-
Weak secrets management
Understanding these risks is the first step toward securing Kubernetes effectively.
A Guide to Become a DevOps Engineer in 2026 (Skills, Roadmap & Salary)
Core Kubernetes Security Principles (2026)
Before diving into tools, every organization should follow these foundational principles:
-
Zero Trust Architecture
-
Least Privilege Access
-
Defense in Depth
-
Shift-Left Security
-
Continuous Monitoring
These principles guide every security decision in Kubernetes environments.
1. Secure Kubernetes Cluster Configuration
Best Practices
-
Disable anonymous access to the API server
-
Use TLS encryption everywhere
-
Secure etcd with encryption at rest
-
Restrict access to the control plane
-
Regularly update Kubernetes versions
A hardened cluster reduces attack surfaces significantly. CIS Kubernetes security benchmark
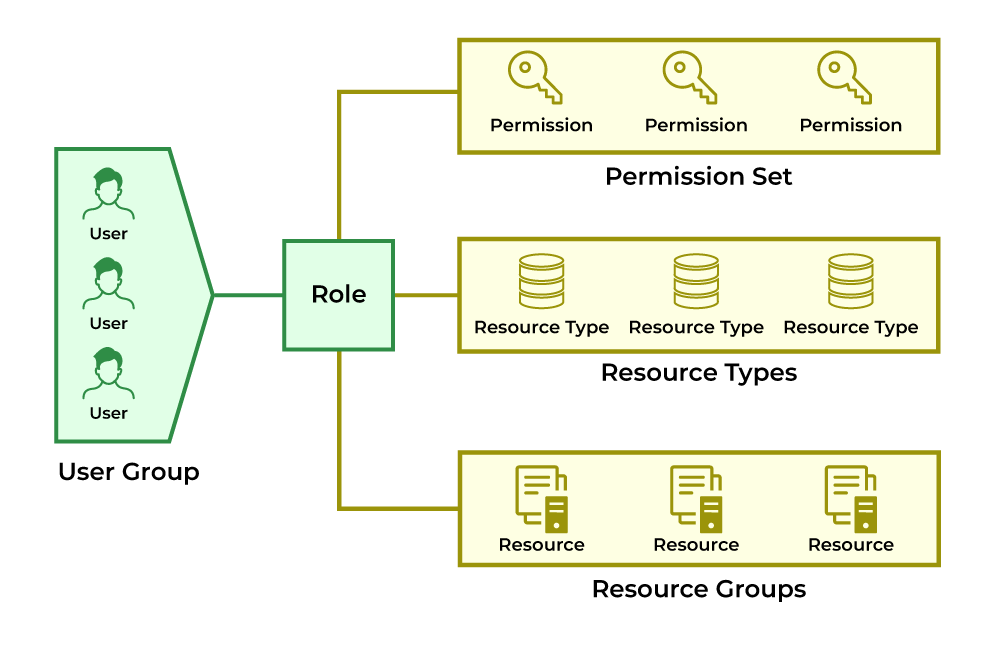
2. Strong Identity, Authentication, and RBAC
RBAC Best Practices
-
Follow least privilege access
-
Avoid wildcard permissions
-
Separate human and service accounts
-
Rotate credentials frequently
-
Integrate with enterprise IAM (OIDC, SSO)
RBAC misconfigurations remain the #1 Kubernetes security issue.
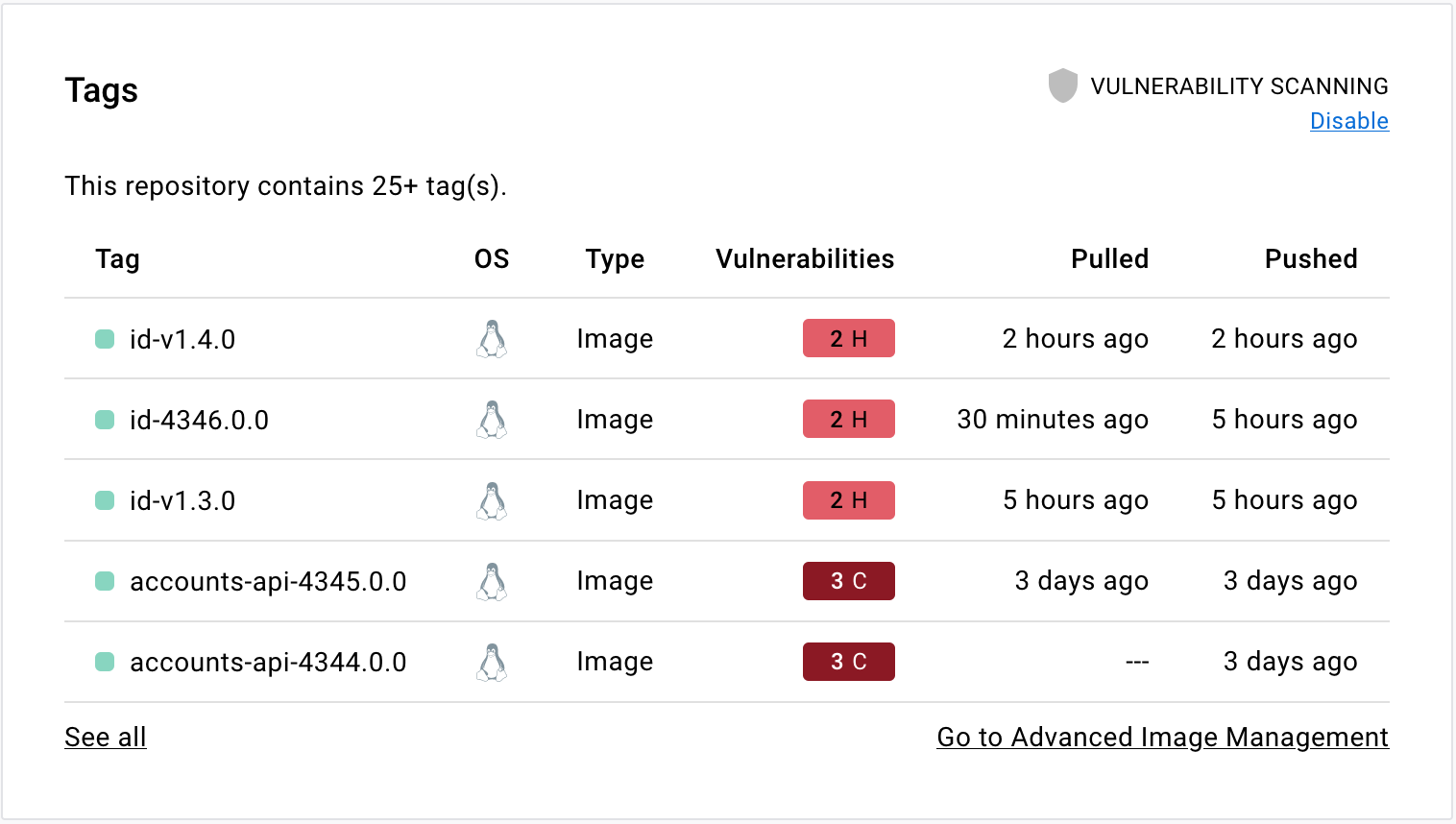
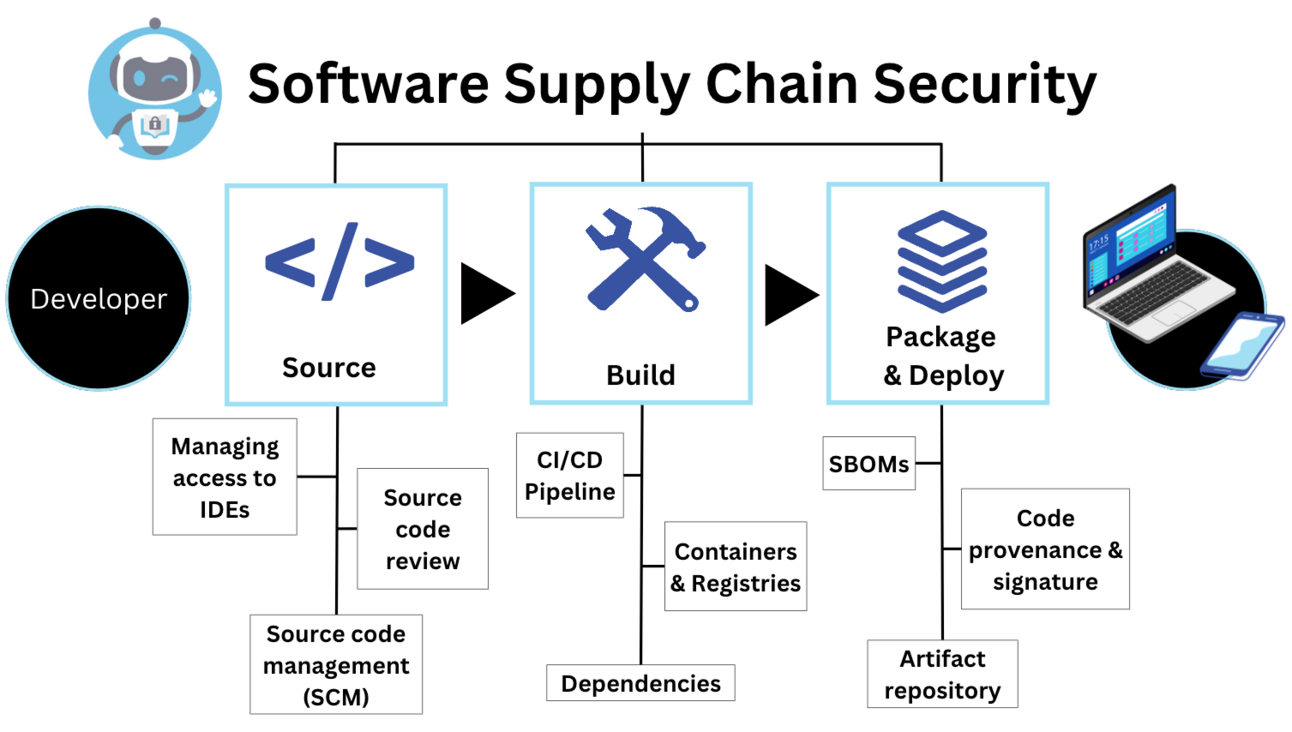
3. Secure Container Images and Supply Chain
Image Security Practices
-
Use minimal base images (distroless, alpine)
-
Scan images for vulnerabilities
-
Sign and verify container images
-
Enforce trusted registries only
-
Automate security checks in CI/CD
Supply-chain attacks are one of the fastest-growing threats in 2026.
4. Network Security and Kubernetes Network Policies
Network Security Best Practices
-
Use Kubernetes Network Policies
-
Enforce pod-to-pod isolation
-
Restrict ingress and egress traffic
-
Use service mesh for encryption (mTLS)
-
Protect external access with WAFs
Network segmentation prevents lateral movement during attacks.
5. Secrets Management and Data Protection
Best Practices
-
Never store secrets in plaintext YAML
-
Use external secret managers
-
Encrypt secrets at rest
-
Rotate secrets automatically
-
Limit secret access via RBAC
Poor secrets management can compromise entire clusters instantly.
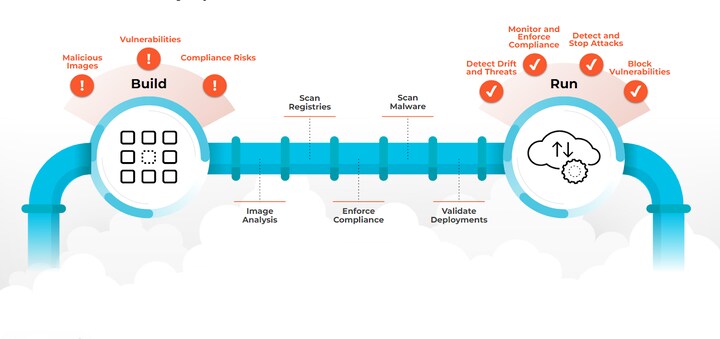
6. Runtime Security and Threat Detection
Runtime Security Measures
-
Monitor system calls
-
Detect abnormal container behavior
-
Enforce runtime policies
-
Alert on privilege escalation attempts
Runtime security helps detect attacks that bypass prevention controls.
7. Logging, Monitoring, and Observability
Monitoring Best Practices
-
Centralize logs
-
Monitor Kubernetes audit logs
-
Track API access
-
Integrate with SIEM tools
-
Set real-time alerts
Visibility is critical for rapid incident response.
Best Kubernetes Security Tools in 2026
🔐 Cluster & Configuration Security
-
kube-bench
-
kube-hunter
-
OPA / Gatekeeper
-
Kyverno
🛡️ Container & Supply Chain Security
-
Trivy
-
Aqua Security
-
Anchore
-
Snyk
🚨 Runtime Security
-
Falco
-
Sysdig Secure
-
CrowdStrike Falcon
🔍 Monitoring & Observability
-
Prometheus + Grafana
-
Datadog
-
Elastic Stack
-
Splunk
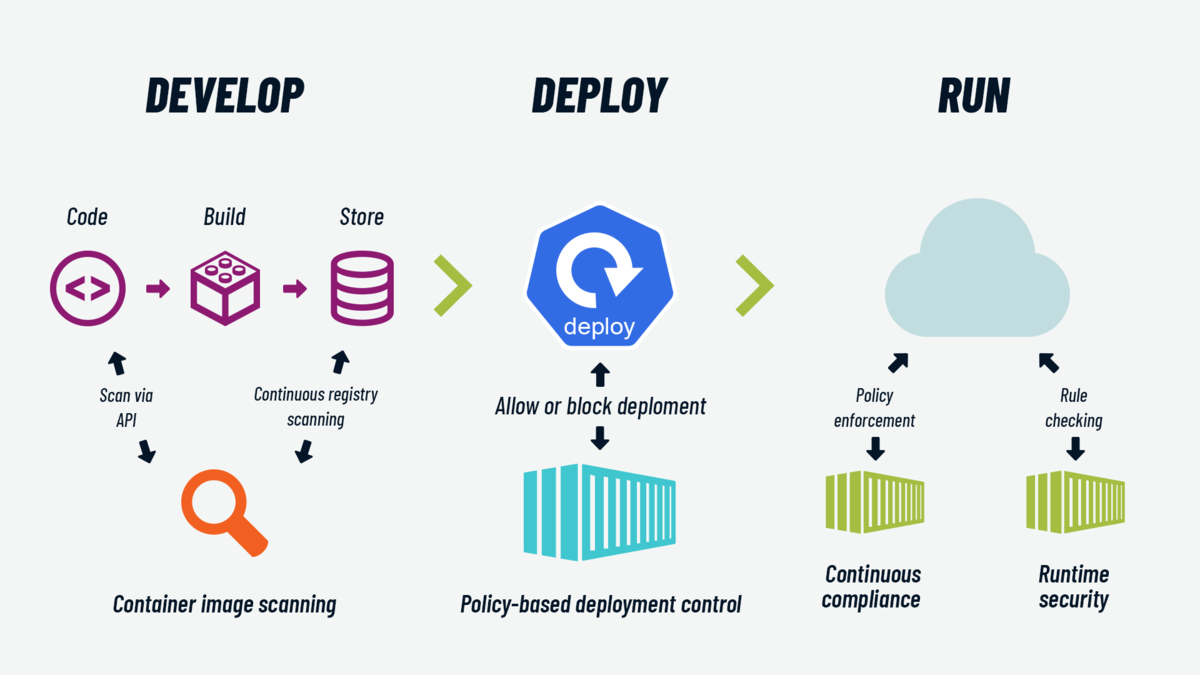
DevSecOps: Integrating Security Into CI/CD
DevSecOps Best Practices
-
Security scans on every commit
-
Policy enforcement before deployment
-
Automated compliance checks
-
Continuous vulnerability scanning
Security should be automated, not manual.
Common Kubernetes Security Mistakes to Avoid
-
Running containers as root
-
Overly permissive RBAC roles
-
Skipping vulnerability scans
-
Ignoring runtime security
-
Hardcoding secrets
-
Delaying cluster updates
Avoiding these mistakes prevents most real-world breaches.
Kubernetes Security Trends Beyond 2026
Key trends shaping the future:
-
AI-driven threat detection
-
Policy-as-code everywhere
-
Platform engineering security
-
Unified cloud security platforms
-
Compliance automation
Kubernetes security is evolving toward intelligent, automated defense.
Conclusion
In 2026, Kubernetes security requires a layered, proactive, and automated approach. By combining strong security practices with modern tooling, organizations can safely scale containerized workloads without compromising performance or agility.
Security is not a blocker—it is an enabler of trust and scalability in cloud-native systems.
















Pingback: How to Make a Monthly Budget (Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners) - Nxtainews