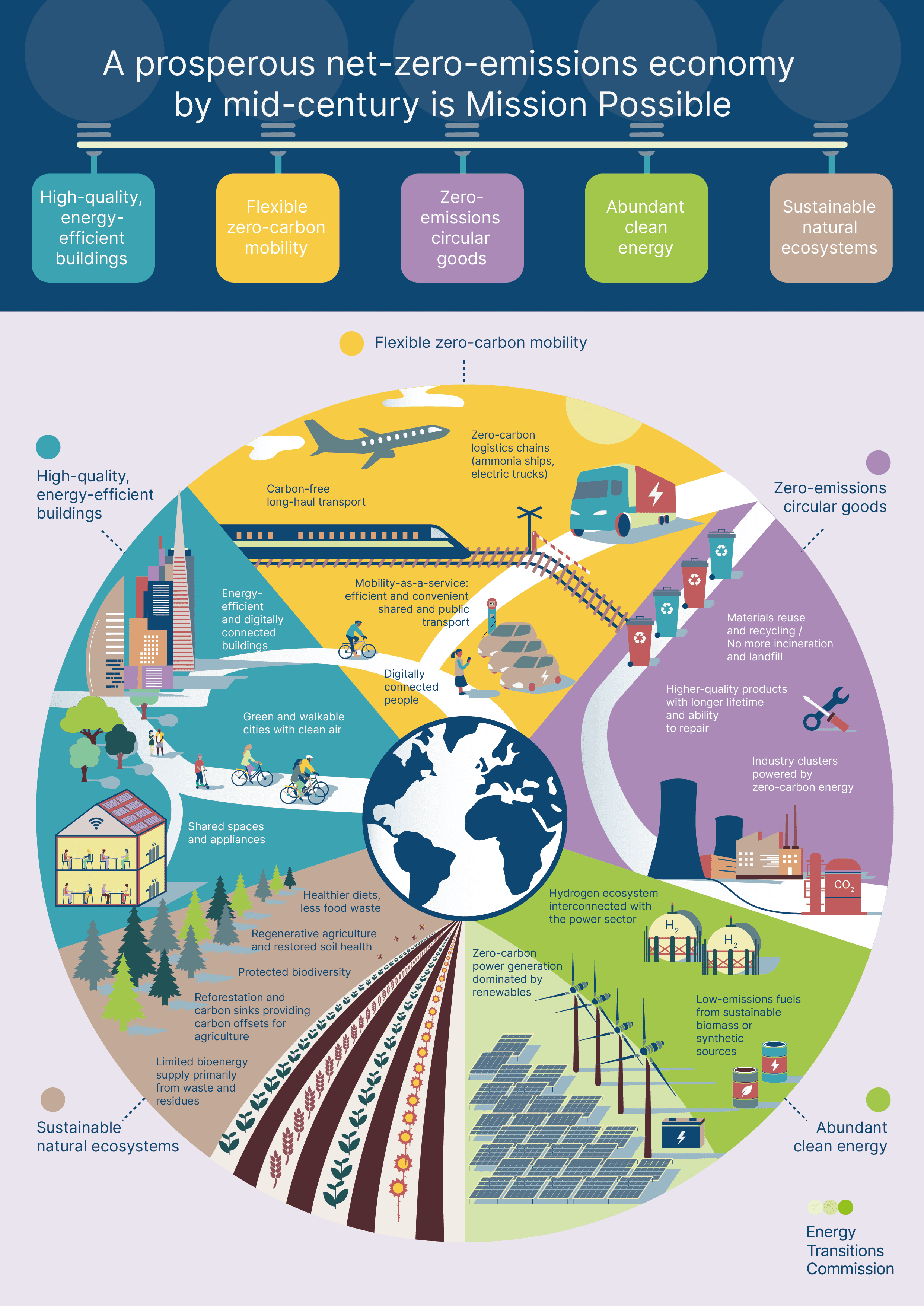
Introduction
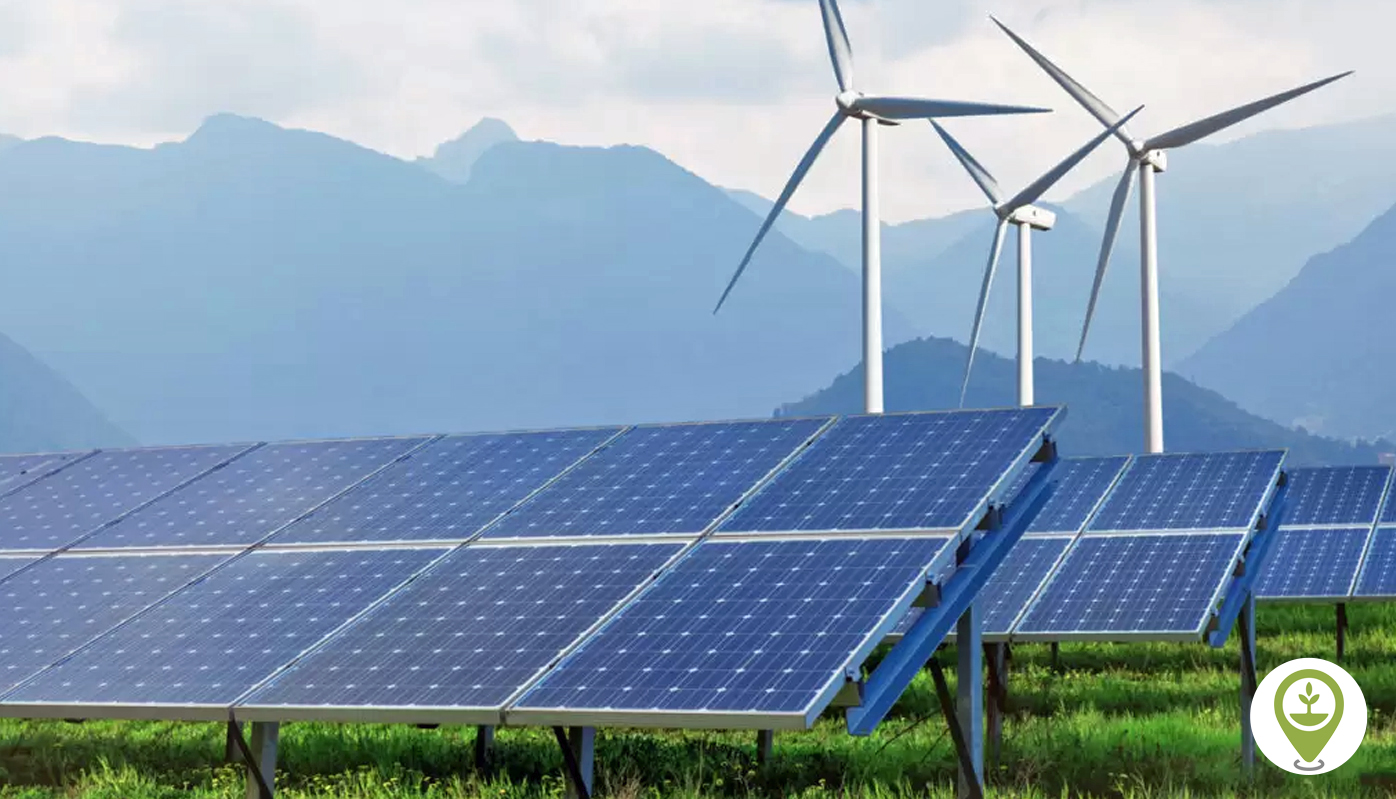
As the world confronts climate change, rising energy demand, and fossil fuel volatility, Renewable Energy Explained has emerged as one of the most important solutions for a sustainable future. Solar panels on rooftops, wind turbines across open landscapes, and massive renewable power plants are becoming symbols of a global energy transition.
But what exactly is renewable energy? How do solar and wind power work, and can they realistically replace fossil fuels? More importantly, what role will clean power play in the future of the global economy?
This article explains renewable energy in simple terms, focusing on solar and wind power, their benefits, limitations, and why they are central to the future of clean energy.
What Is Renewable Energy?
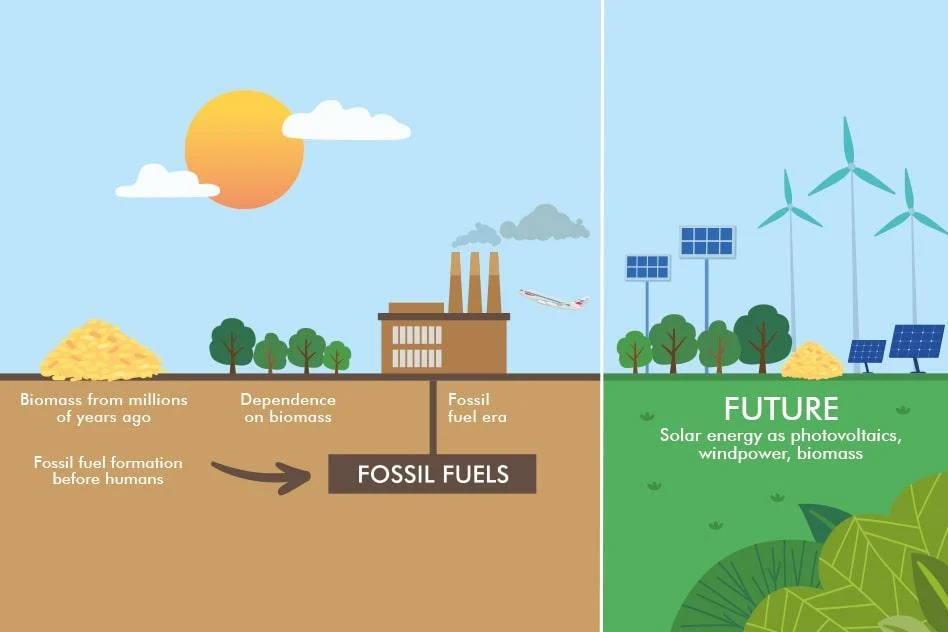
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that are constantly replenished and do not run out. Unlike coal, oil, and gas, renewables generate energy without permanently depleting resources or releasing large amounts of greenhouse gases.
Electric Vehicles and Climate Change: Are EVs Really Better?
Main Types of Renewable Energy
-
Solar energy
-
Wind energy
-
Hydropower
-
Geothermal energy
-
Biomass energy
Among these, solar and wind are the fastest-growing and most widely adopted sources worldwide.
International Energy Agency – Renewable Energy
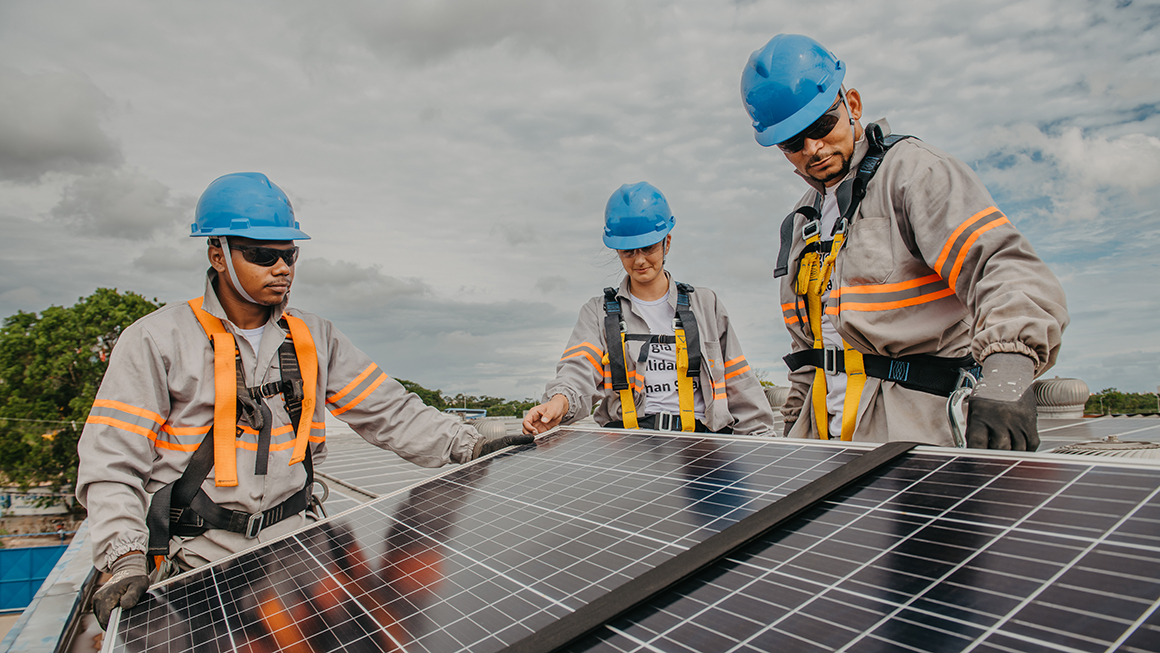
Solar Energy Explained
How Solar Power Works
Solar energy is generated using photovoltaic (PV) panels that convert sunlight directly into electricity. When sunlight hits the solar cells, it creates an electric current that can power homes, businesses, and even entire cities.
United Nations – Renewable Energy and Climate Action
Types of Solar Energy
-
Rooftop solar: Installed on homes and buildings
-
Utility-scale solar farms: Large installations generating power for the grid
-
Solar thermal: Uses heat from the sun to produce energy
Advantages of Solar Power
-
Zero emissions during operation
-
Abundant and widely available
-
Low operating and maintenance costs
-
Scalable—from small homes to massive power plants
Challenges of Solar Energy
-
Intermittent (depends on sunlight)
-
Requires energy storage solutions
-
Initial installation costs
Despite these challenges, solar energy has become one of the cheapest sources of electricity in many parts of the world.
Wind Energy Explained
How Wind Power Works
Wind turbines capture the kinetic energy of moving air and convert it into electricity. As wind turns the turbine blades, a generator produces power that feeds into the electric grid.
Types of Wind Energy
-
Onshore wind: Installed on land
-
Offshore wind: Built in oceans or large lakes, offering stronger and more consistent winds
Advantages of Wind Power
-
Clean and renewable
-
Highly efficient
-
Large-scale electricity generation
-
Minimal land disruption (land can still be used for farming)
Challenges of Wind Energy
-
Visual and noise concerns
-
Wildlife impact if poorly planned
-
Variability in wind availability
Overall, wind energy is one of the most cost-effective renewable sources today.
Solar and Wind vs Fossil Fuels
Environmental Impact
-
Fossil fuels emit large amounts of CO₂ and pollutants
-
Solar and wind produce near-zero emissions during operation
Economic Impact
-
Fossil fuels face volatile prices
-
Renewables offer long-term price stability
Energy Security
-
Fossil fuels rely on imports and geopolitics
-
Renewables use local natural resources
Renewable energy reduces pollution, lowers health costs, and strengthens energy independence.
The Role of Renewable Energy in Climate Change
Renewable energy is essential to achieving:
-
Carbon neutrality
-
Net zero emissions
-
Climate change mitigation goals
Switching to clean power helps:
-
Reduce greenhouse gas emissions
-
Limit global warming
-
Support sustainable development
Without renewables, meeting global climate targets would be nearly impossible.
Energy Storage and the Future of Clean Power
One major challenge for solar and wind is intermittency. This is where energy storage becomes critical.
Key Storage Solutions
-
Lithium-ion batteries
-
Grid-scale battery systems
-
Pumped hydro storage
-
Emerging technologies (hydrogen, solid-state batteries)
As storage technology improves, renewable energy will become more reliable and widely adopted.
Economic and Job Benefits of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy is not just an environmental solution—it is an economic opportunity.
Key Benefits
-
Millions of new jobs worldwide
-
Growth of the green economy
-
Lower energy costs over time
-
Innovation and technological leadership
Countries investing early in renewables are positioning themselves as future energy leaders.
Challenges Facing Renewable Energy
Despite rapid progress, challenges remain:
-
Grid infrastructure upgrades
-
Energy storage scalability
-
Policy and regulatory barriers
-
Initial investment costs
However, continued innovation and policy support are steadily addressing these issues.
The Future of Renewable Energy
The future of clean power is increasingly clear:
-
Solar and wind will dominate new energy capacity
-
Fossil fuel use will continue to decline
-
Energy systems will become cleaner, smarter, and more decentralized
Renewable energy is no longer an alternative—it is becoming the foundation of the global energy system.
Conclusion
Renewable energy—especially solar and wind—represents the future of clean power. While challenges remain, technological advances, falling costs, and global climate commitments are accelerating the transition away from fossil fuels.
As the world moves toward net zero emissions, renewable energy will play a central role in powering economies, protecting the environment, and shaping a sustainable future for generations to come.





























Pingback: Artificial Intelligence and Climate Change: Can AI Save the Planet? - Nxtainews